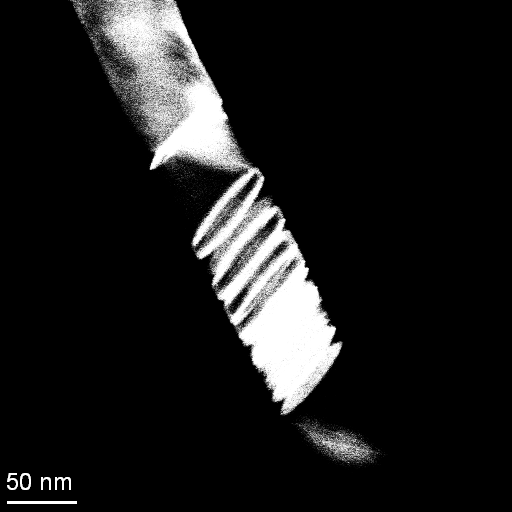
A significant study from our research team, titled “Unravelling Nanometallurgy with In Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Case Study with Copper Nanowires,” was recently published in Nano Today. Led by Diego Coradini, our former PhD student, the research delves into the behavior of copper nanowires under extreme heating conditions within a transmission electron microscope. By focusing on nanowires with diameters between 40 and 140 nm, the study revealed key insights into the effects of sublimation and surface diffusion at temperatures as low as 923 K. These findings give a deeper understanding of thermal behavior in nanoscale materials, which is crucial for advancing applications in electronics and beyond.
This work shows an important step in the development of nanometallurgy, a field that redefines traditional metallurgical concepts for nanoscale applications. Through the use of advanced electron microscopy, our team demonstrated how atomic-level processes in nanomaterials can be analyzed, opening new pathways for innovation in material science. This research emphasizes the importance of understanding surface effects and nanoscale behavior, laying a foundation for future advancements in material design and applications in extreme environments.
The work from Diego completes the trilogy of nanometallurgy in our laboratory in Austria. This is an interesting fundamental research and an emerging science we started here in Leoben in 2020. Do not forget to read all the three papers on nanometallurgy (all open access):

1. D.S.R. Coradini, M.A. Tunes et al. Degradation of Cu nanowires in a low-reactive plasma environment. npj Materials degradation, v. 4, n. 1, 33, 2020. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41529-020-00137-2
2. D.S.R. Coradini, M.A. Tunes et al. In situ transmission electron microscopy as a toolbox for the emerging science of nanometallurgy. Lab on a Chip 23.14, 3186-3193, 2023. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2023/lc/d3lc00228d
3. D.S.R. Coradini, M.A. Tunes et al. Unravelling nanometallurgy with in situtransmission electron microscopy: A case-study with copper nanowires. Nano Today 59, 102485, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102485


